Historical Background and Role
The HNODC was established in 1986, in the frame of the cooperation of Greece with the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC). It is a national agency, part of the international network of NODCs, operating within the framework of IOC/IODE. It participates in different elements of the IODE system, icluding, acquiring, formatting, quality controlling, cataloguing, archiving, disseminating and exchanging of marine data and information. HNODC also operates within the framework of Hellenic Centre for Marine Research (HCMR), in Anavyssos (Attika) and it is recognized as a national facility for international data and information exchange.
Furthermore it promotes the International Exchange of Data in the frame of its cooperation with the “Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC ) of UNESCO as it is responsible for the coordination of International Data Exchange ( IODE ) in Greece.
Major Data Holdings
HNODC holds a great diversity of different data types that come from several Research Institutes and mainly by HCMR and also the participation of HNODC in National, European and International Programmes.
All data are subjected to quality control procedures according to the International standards as these agreed during EU Projects and International Organizations.
A mass volume of over 320.000 station data concerning physical, chemical and biological Oceanographic information, have been stored.
The latest progress in data collection is that HNODC data base is currently hosting data from the POSEIDON system (http://poseidon.hcmr.gr/) which is a monitoring, forecasting and Information system for the greek seas.
Poseidon is based on an established network of observation buoys (Figure 1). The network of observation buoys records continuously the physical, biological and chemical parameters of the Greek seas. Those data are then transmitted to the operational centre where they are sorted and fed into forecasting models.
The Architecture
A three layers architecture was used that can be denoted as follows:
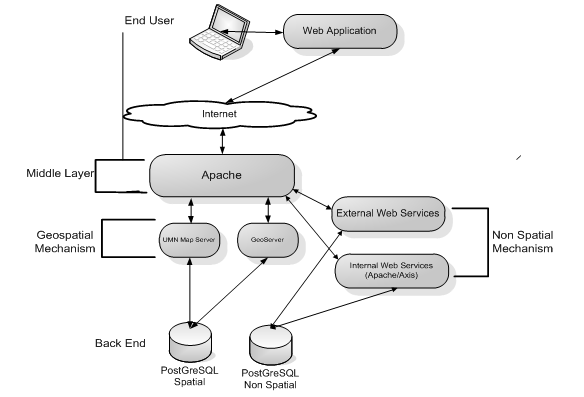
- At the Back end layer Open Source PostgreSQL DBMS (and not only..) stands as the data storage mechanism with more than one Data Base Schemas. UMN Map Server and Geoserver are the mechanisms for:
- representing geographically geospatial data and metadata information via the Web Map Service (WMS),
- querying and navigating Geospatial and Meta data via the Web Feature Service (WFS),
- transacting and processing new or existing Geospatial Data via the Web Processing Service (WPS), in the near future.
- WhereGroup MapBender, a geospatial portal site management software for OGC and OWS architectures, acts as the integration module between the Geospatial Mechanisms.
- Apache and Tomcat stand as the Web Service middle Layers. Apache Axis2 with its embedded implementation of the SOAP protocol acts as the No spatial data Mechanism of Web Services. (These modules of the platform are still under development but their implementation will be completed in the near future.)
- In the presentation layer a Web user Interface has been developed based on enhanced and customized version of a Mapbender GUI. This application is an online Search, Map and download service. allows searching, visualizing and downloading data from the Hellenic oceanographic data base.
Main Facilities
HNODC provides data and services using an advanced, continuously upgraded, hardware and software computing environment.
Networking Environment:
- HNODC is connected to National Academic network with 1 Gbps fiberoptic line.
- Localy a gigabit lan is implemeneted with a 280 Gbps backplain core layer3 switch (HP 9308M) and several border switches.
- Network is protected by firewall and IDS system and is monitored using Nagios monitoring system.
- Dial up remote access and VPN services are provided as well.
- cloud storage service
Computing Environment:
- Hardware: Is based on several LINUX and UNIX servers, working as stand alone servers, clusters or virtual machines. Fail safe is implemented (in hardware level) using SAN RAID 5 devices.
- Software: Oracle, Mysql and Pqsql RDBMS systems with Geospatial extensions. Mapserver, Geoserver and Geotools are used to provide Geospatial access to data. Many software products are used for back office support, image processing, and data modeling.
-
PHP, PERL, C, Java, Fortran, programming languages
Menu
Events Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |||
SeaDataNet
SeaDataNet has developed an efficient distributed Marine Data Management Infrastructure for the management of large and diverse sets of data deriving from in situ and remote observation of the seas and oceans.
Professional data centres, active in data collection, constitute a Pan-European network providing on-line integrated databases of standardized quality.
IODE
The programme "International Oceanographic Data and Information Exchange" (IODE) of the "Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission" (IOC) of UNESCO was established in 1961. Its purpose is to enhance marine research, exploitation and development, by facilitating the exchange of oceanographic data and information between participating Member States, and by meeting the needs of users for data and information products.
EMODnet Seabed Mapping
The European Commission, represented for the purposes of this project by the Directorate-General for Maritime Affairs and Fisheries (DG MARE), has concluded service contracts for creating pilot components of the European Marine Observation and Data Network (EMODnet). The overall objective is to create pilots to migrate fragmented and inaccessible marine data into interoperable, continuous and publicly available data streams for complete maritime basins. The results will help to define processes, best technology and approximate costs of a final operational European Marine Observation and Data Network.
ODIP
The ODIP project is a Coordination and Support Action of the Research Infrastructures programme within EU FP7. The contract number is 312492. It has a duration of 36 months from 1st October 2012 till 31st September 2015.
Ocean and marine data are recognised as valuable resources which have a high cost of acquisition and as such should be well managed and made as widely available to end users as possible for a variety of uses including scientific research, marine management and planning, policy and decision making, and economic activities.
